Psoriasis
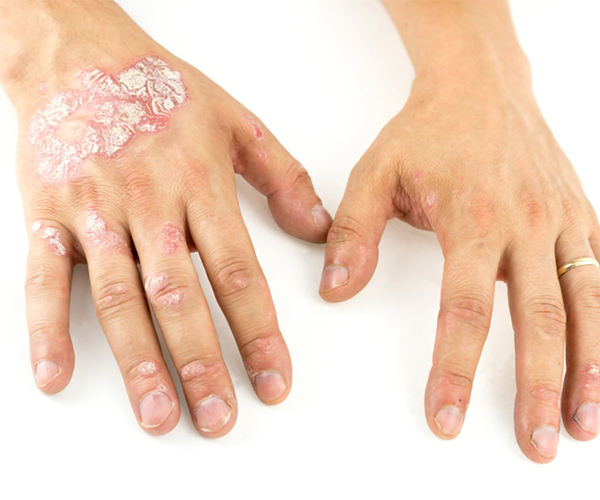
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the skin, leading to the rapid growth of skin cells. Normally, skin cells grow and shed in a cycle that takes about a month, but in people with psoriasis, this process is accelerated. The new skin cells build up, forming thick, scaly patches that can appear red, silvery, or white. These patches can develop anywhere on the body but are most common on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be linked to an immune system malfunction, where the body mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing inflammation and rapid skin turnover.

symptoms
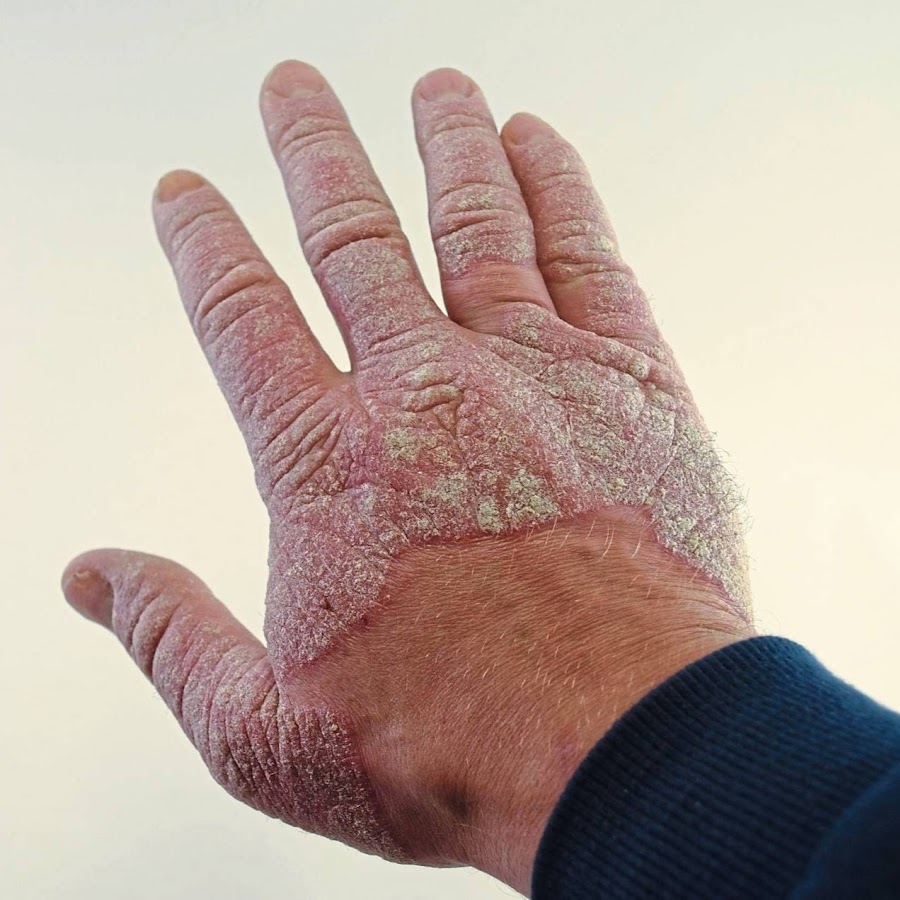

The symptoms of psoriasis vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. The most common form is plaque psoriasis, characterized by raised, red patches covered with silvery-white scales. Psoriasis can also manifest as guttate psoriasis (small, drop-like lesions), inverse psoriasis (smooth, red patches in skin folds), pustular psoriasis (white pustules surrounded by red skin), or erythrodermic psoriasis (a rare, severe form that causes widespread redness and peeling). Itching, burning, and soreness often accompany these patches, and the condition can lead to discomfort, reduced mobility, and an increased risk of infections.
Treatments
Psoriasis is a chronic condition, meaning that it cannot be cured, but its symptoms can be managed. Treatment typically involves a combination of topical treatments, phototherapy, and systemic therapies.
topical treatments and phototherapy
Topical treatments are usually the first line of defense. These include corticosteroids, which reduce inflammation, and other medications like vitamin D analogs, coal tar,or topical retinoids, which help slow down the rapid skin cell turnover. Newer topical steroid-free therapies such as tapinarof (Vtama) cream and roflumilast (Zoryve) cream are also extremely effective in reducing inflammation, especially in sensitive areas of the skin. Phototherapy (also known as light therapy) involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under controlled conditions. This can help reduce symptoms by slowing skin cell production and reducing inflammation.
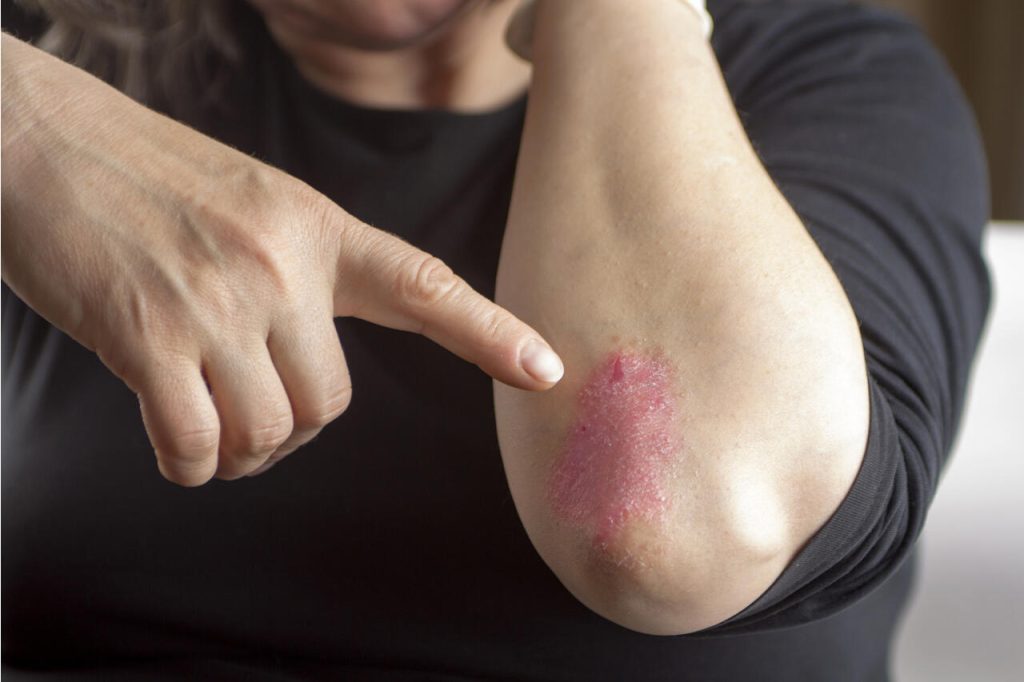
systemic treatments
In cases where topical treatments and phototherapy do not provide adequate relief, systemic treatments may be recommended. These include oral medications such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or acitretin, which work to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation. Biologic drugs are a newer class of treatments administered by injection or infusion. They target specific immune system proteins that contribute to Psoriasis, offering relief for people with moderate to severe cases. Biologics include drugs like TNF inhibitors, IL-12, IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors and JAK 2 inhibitors. These medications are often prescribed when psoriasis severely impacts a person’s quality of life or when other treatments have not been effective.
highly individualized treatment plan
At Aesthetic Dermatology,the treatment plan for psoriasis is highly individualized. We will assess the severity and type of psoriasis and recommend the most appropriate therapy. We may also provide advice on lifestyle changes, such as moisturizing the skin regularly to prevent dryness, avoiding triggers like stress or certain medications, and sun protection. Since psoriasis is a chronic condition with periods of flare-ups and remission, ongoing monitoring and adjustment of treatment may be necessary. In some cases, additional treatments like lifestyle adjustments or addressing comorbid conditions (such as arthritis, which is common in those with psoriasis) may also be part of the overall management plan.
Improved Skin Texture
Improved Skin Tone and Clarity
Combatting Acne and Blackheads
Boosting Collagen Production
Minimal Downtime and Quick Results
Get in Touch
Do Not Hesitate




